In a recent article published by the 388th Fighter Wing Public Affairs on February 15, 2019, an update was provided on Red Flag-19-1 and how the impact of the F-35 is changing the approach to air combat.
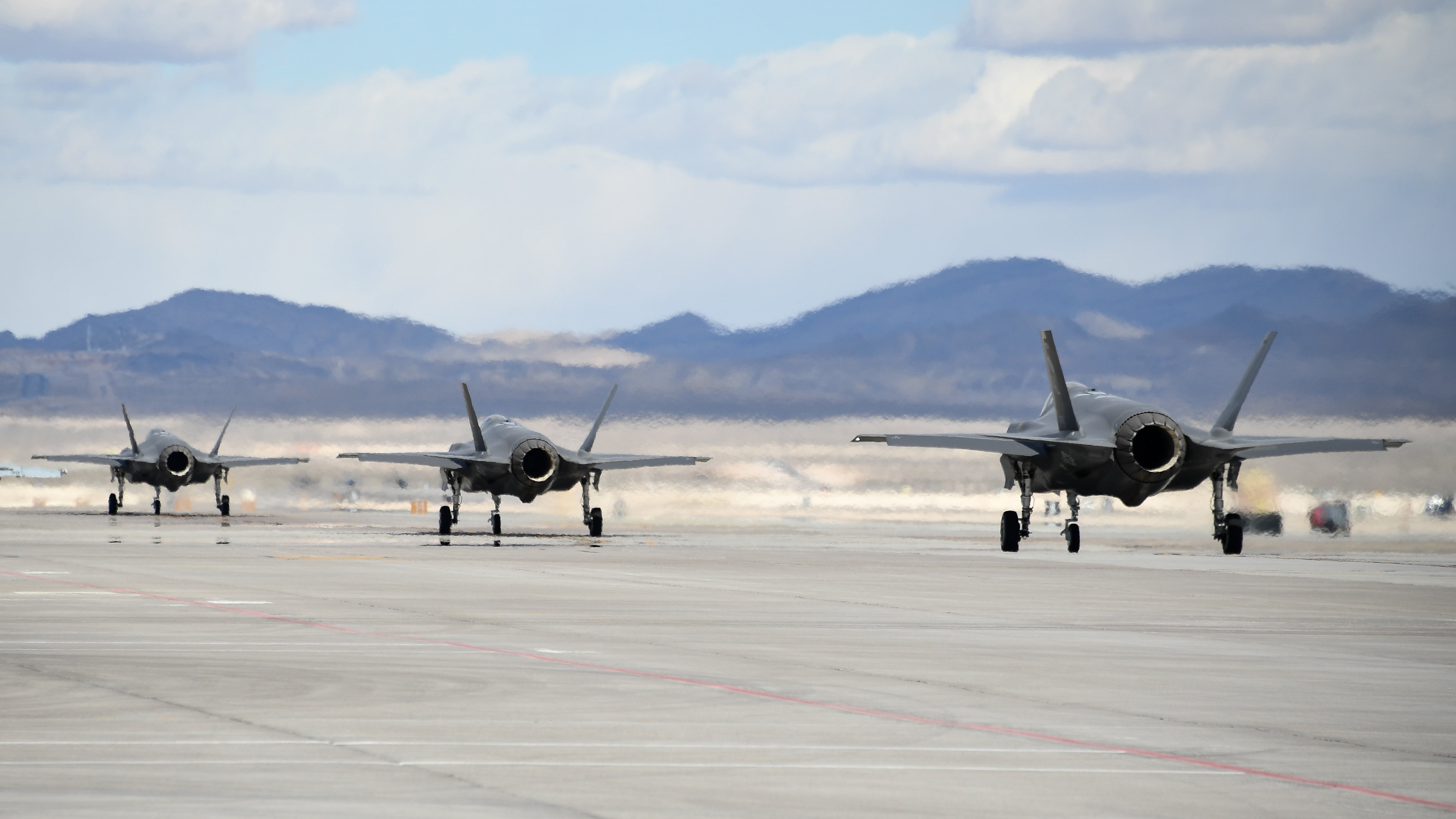
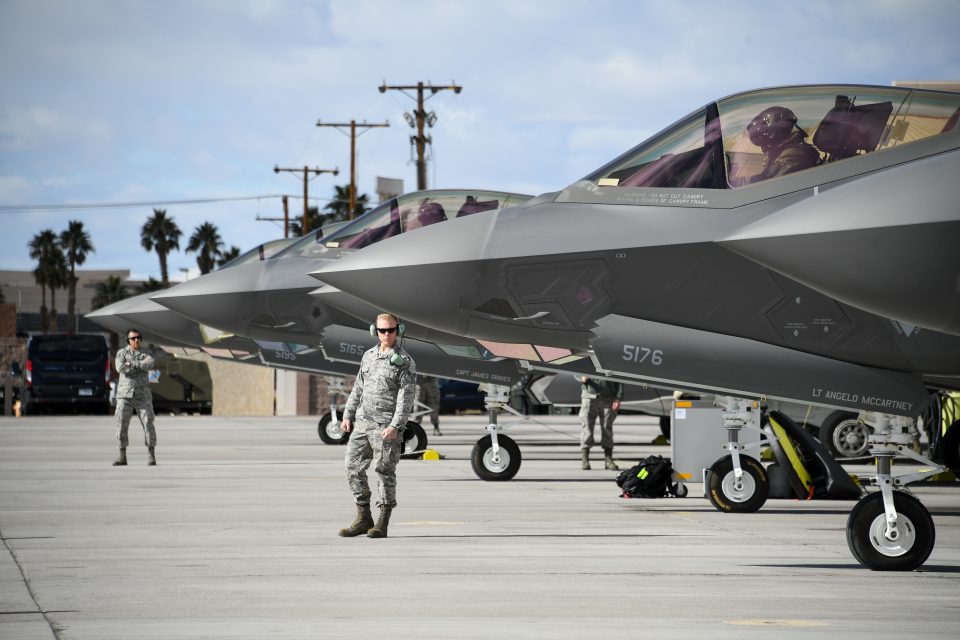
Today, Airmen from the 388th Fighter Wing’s 4th Fighter Squadron wrapped up flying operations with the F-35A Lightning II in an “exponentially more challenging” Red Flag.
The 4th FS integrated the F-35A into a large, capable “Blue Force” in diverse missions against an equally capable “Red Force.” Nearly 3,000 personnel from 39 separate units participated in the exercise, including the U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, Royal Air Force and Royal Australian Air Force.
The Red Force was made up of hybrid threats, combinations of the “most advanced weapons systems out there,” meant to replicate “near-peer” enemies in a large scale conflict. The shift closely aligns with the National Defense Strategy.
“The first time I came to Red Flag in 2004, our tactics were the same as they had been since the early 1980s. Now, the threat and complexity are at a whole different level,” said Col. Joshua Wood, 388th Operations Group commander. “It’s no longer assumed that we will gain and maintain air superiority. That’s a big shift.”
Red Flag aggressors encompass the whole spectrum of an adversary force – advanced integrated air-defense systems, an adversary air force, cyber-warfare and information operations. Because of these diverse capabilities, many Red Flag missions are flown in “contested or denied” environments with active electronic attack, communications jamming, and GPS denial.
“Those situations highlight the fifth-generation capabilities of the F-35. We’re still able to operate and be successful. In a lot of cases we have a large role as an integrated quarterback,” said Lt. Col. Yosef Morris, 4th Fighter Squadron commander. “Our ability to continue to fuse and pass information to the entire package makes every aircraft more survivable.”
During the first week of Red Flag, the F-35 pilots flew in a larger force of Blue Air in a counter-air mission. More than 60 aggressor aircraft were flying against them, blinding many of the fourth-generation aircraft with “robust” electronic attack capabilities.
“I’ve never seen anything like it before.” Wood said. “This is not a mission you want a young pilot flying in. My wingman was a brand new F-35A pilot, seven or eight flights out of training. He gets on the radio and tells an experienced, 3,000-hour pilot in a very capable fourth-generation aircraft. ‘Hey bud, you need to turn around. You’re about to die. There’s a threat off your nose.’”
The young pilot then “killed” the enemy aircraft and had three more kills in the hour-long mission.
“Even in this extremely challenging environment, the F-35 didn’t have many difficulties doing its job,” Wood said. ‘That’s a testament to the pilot’s training and the capabilities of the jet.”
One of the most valuable things about this exercise for the 4th Fighter Squadron is the experience it provided younger pilots flying combat missions as part of an integrated force. Thirteen pilots in the squadron have never flown the F-35 in Red Flag, and four of them just graduated pilot training.
“They say it’s the most realistic thing to combat,” said 1st Lt. Landon Moores, a new F-35A pilot. “It’s been pretty intense.”
Red Flag is not a “rolling campaign.” It is made up of different scenarios that increase in difficulty as the weeks go on. This allows the integrated force to learn how best to capitalize on the strengths and protect the weaknesses of each platform in very specific mission sets.
“With stealth, the F-35 can get closer to threats than many other aircraft can. Combined with the performance of the fused sensors on the F-35, we can significantly contribute to the majority of the missions,” Morris said.
The missions aren’t just 90-minute flights. They require 12-hours of intense planning the day prior, a two hour pre-brief, and then several hours of debriefing after the mission – dissecting the outcome and looking for ways to improve.
“It’s not like we just come back and high-five if we’re successful,” Morris said. “Could we have done better? Did we have all the resources we needed? Often the brief and debrief is the most valuable part of Red Flag, especially for younger pilots.”
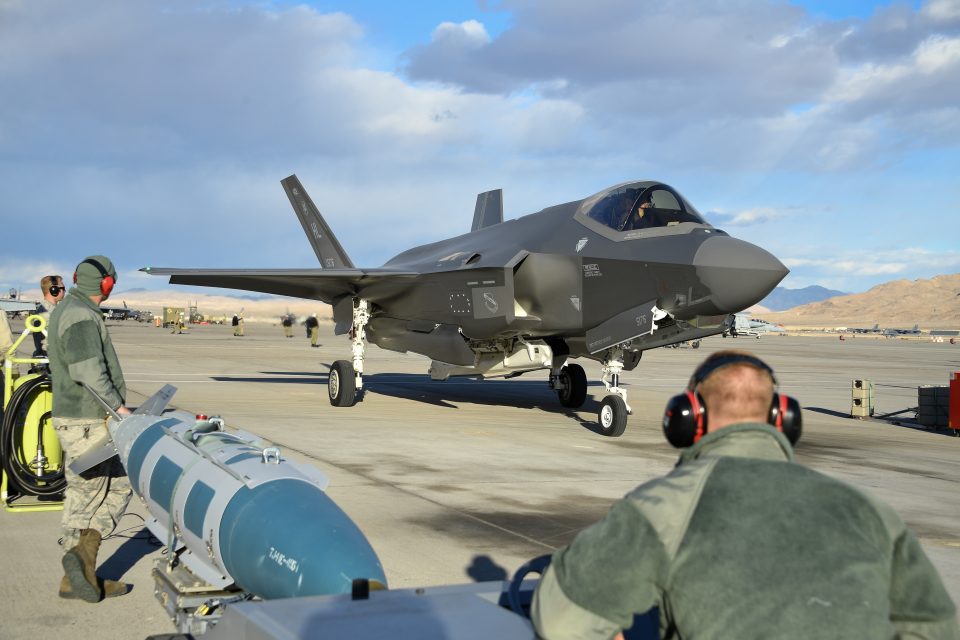
The squadron brought 12 aircraft and more than 200 Airmen to the three-week exercise – pilots, maintainers, intelligence officers, weapons crews, and support personnel, including reservists from the 419th Fighter Wing. Maintainers didn’t lose a single sortie to a maintenance ground-abort and had spare aircraft available for every mission.
“As this aircraft matures, we continue to see it be a significant force-multiplier in a threat-dense environment,” Morris said. “Red Flag was a success for us and has made our younger pilots more lethal and more confident.”