By Ed Timperlake
The famous battle winning lineage of the Navy’s Anti-submarine force (ASW) is being called to “Sound General Quarters Battle Stations” because America is being directly threatened by the President of Russia’s submarines with low flying air-breathing nuclear tipped hypersonic cruise missiles.
The significant change in the direct threat to the United States which the Trump Administration has highlighted in last year’s National Security strategy was presaged by the NORAD/NORTHCOM Commander Admiral Bill Gortney, a clear embodiment of the fighting navy, in our 2016 interview with him in his office at Colorado Springs.
Question: The Russians are not the Soviets, but they are generating new capabilities, which clearly provide a need to rethink homeland defense.
How would you characterize the Russian dynamic?
Answer: With the emergence of the new Russia, they are developing a qualitatively better military than the quantitative military that they had in the Soviet Union.
They have a doctrine to support that wholly government doctrine. And you’re seeing that doctrine in military capability being employed in the Ukraine and in Syria.
For example, the Russians are evolving their long-range aviation and at sea capabilities. They are fielding and employing precision-guided cruise missiles from the air, from ships and from submarines.
Their new cruise missiles can be launched from Bears and Blackjacks and they went from development to testing by use in Syria. It achieved initial operating capability based on a shot from a deployed force.
The Kh-101 and 102 were in development, not testing, so they used combat shots as “tests,” which means that their capability for technological “surprise” is significant as well, as their force evolves.
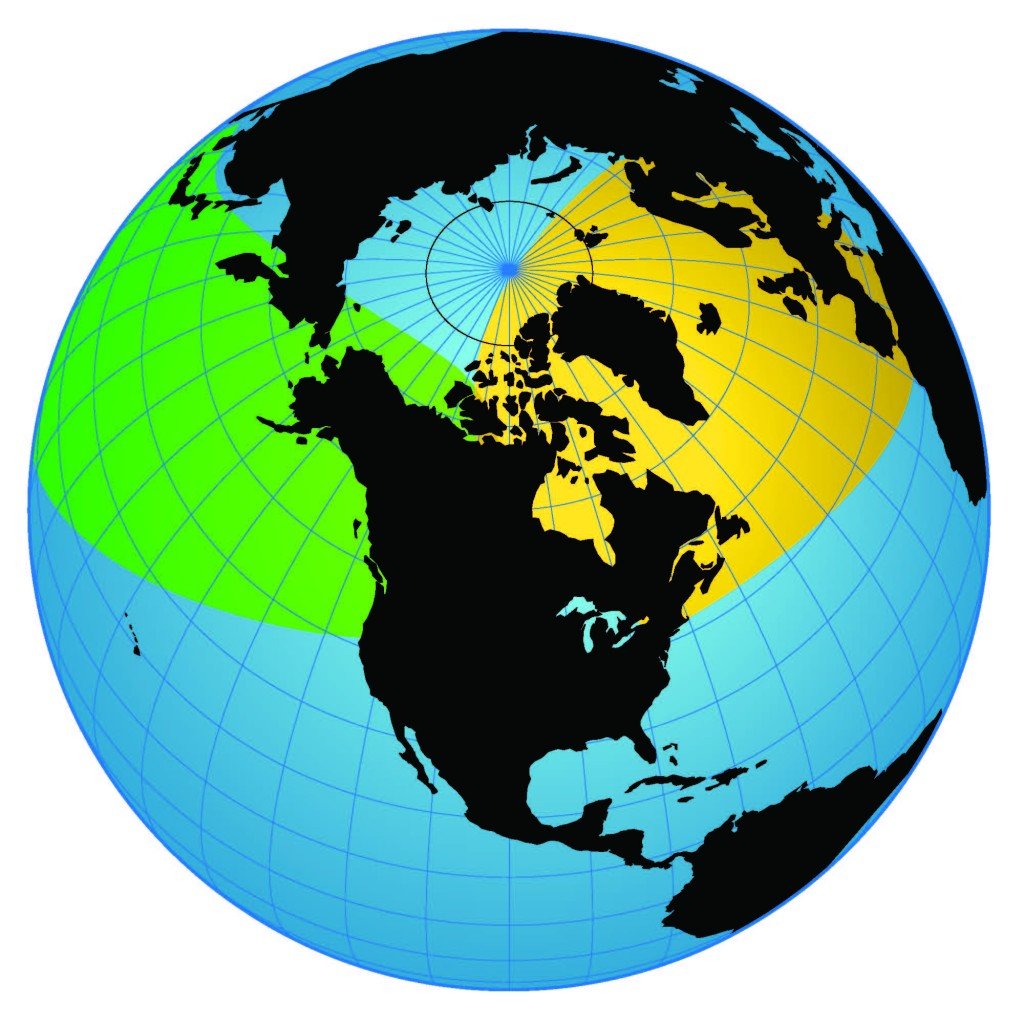
The air and sea-launched cruise missiles can carry conventional or nuclear warheads, and what this means is that a “tactical” weapon can have strategic effect with regard to North America.
Today, they can launch from their air bases over Russia and reach into North American territory.
The challenge is that, when launched, we are catching arrows, but we are not going after the archers.
The archers do not have to leave Russia in order to range our homeland.
And with the augmentation of the firepower of their submarine force, the question of the state of our anti-submarine warfare capabilities is clearly raised by in the North Atlantic and the Northern Pacific waters.
What this means for NORAD as well is that limiting it to air defense limits our ability to deal with the multi-domain threat.
It is an air and maritime threat and you need to go on that tack and defense through multiple domains, not simply the classic air battle.
The NORAD Commander was clearly anticipating the core requirement for an air-sea integrated force to deal with the evolving Russian challenge, including the nuclear one.
Clearly, a key element of shaping an effective warfighting/deterrent force is the evolving US and allied anti-submarine capability.
And it is not just about history but a key element of the training and combat development dynamics of the kill web navy.
The ASW community like their fellow combat Naval Aviators and their SEAL team partners, have been day-in and day out 24/7 “training training training.”
And as we have seen at warfighting centers like Navy Fallon or at Jax Navy where the P-8 has been stood up, training encompasses the dynamics of change for concepts of operations to defeat an enemy fleet.
A key dynamic of change is how the Navy is working surface fleet and air integration to extend the reach and lethality of the fleet and to expand kill web capabilities of the ASW force.
During our visit to Fallon in 2017, Admiral “Hyfi” Harris highlighted the key development and evolving capability:
The SWO boss, Admiral Rowden, has been pretty adamant about the benefits of their Warfighting Development Center, the Surface and Mine Warfighting Development Center.
“SMWDC has been, in my mind, going full bore at developing three different kinds of warfare instructors, WTIs.
“They have an ASW/ASUW, so anti-surface and anti-submarine warfare officer.
“They have an IAMD officer and they have an expeditionary warfare officer.We are watching young lieutenants share with their bosses in a training environment, specifically during IADC (Integrated Air Defense Course).
“This is probably not the way we want AEGIS set up, or how we want the ship to be thinking in an automated mode.
“We may not previously have wanted to go to that next automated step, but we have to because this threat is going to force us into that logic.
And you’re seeing those COs, who were hesitant at first, say, “Now after that run in that event, I get it. I have to think differently.
“Admiral Rowden talks about distributed lethality and they are getting there rapidly.
And the addition of the Triton unmanned system as well as the new P-8s are part of an enhanced airborne detection and strike capability against enemy submarines.
The Navy and several allies are replacing the venerable P-3 with a dyad, the P-8 and the Triton.
During a visit to Jax Navy in 2016, the ASW community there shared their perspectives on the way ahead, which underscored the evolving kill web approach facing Russian submarines seeking to execute the nuclear mission described by President Putin.
Or put in other terms, the Russian President needs to realize that he is not fighting the US Navy of the Cold War years; he is facing a kill web enabled US Navy able to leverage a variety of assets to destroy his maritime assets.
In this sense, we are the reactive enemy against Putin’s declaratory strategy and arms buildup.
We published a report on our visit to Jax Navy in 2016 and provided the following over to the report which outlined key elements of how the Navy was positioning itself to provide building blocks for escalation dominance against peer adversaries.
On May 23 and 24, 2016, during a Jacksonville Naval Air Station visit, we spent time with the P-8 and Triton community which is shaping a common culture guiding the transformation of the ASW and ISR side of Naval Air. The acquisition term for the effort is a “family of systems” whereby the P-3 is being “replaced” by the P-8 and the Triton Remotely Piloted Aircraft.
But clearly the combined capability is a replacement of the P-3 in only one sense – executing the anti-submarine warfare function. But the additional ISR and C2 enterprise being put in place to operate the combined P-8 and Triton capability is a much broader capability than the classic P-3. Much like the Osprey transformed the USMC prior to flying the F-35, the P-8/Triton team is doing the same for the US Navy prior to incorporating the F-35 within the carrier air wing.
In addition to the Wing Commander and his Deputy Commander, who were vey generous with their time and sharing of important insights, we had the opportunity to interviews with various members of the VP-16 P-8 squadron from CO and XO to Pilots, NFOs and Air Crew members, along with the wing weapons and training officer, the Triton FIT team, and key members of the Integrated Training Center. Those interviews will be published over the next few weeks.
The P-8/Triton capability is part of what we have described as 21st century air combat systems: software upgradeable, fleet deployed, currently with a multinational coalition emerging peer partnership. Already the Indians, the Aussies and the British are or will be flying the P-8s and all are in discussions to build commonality from the stand-up of the P-8 Forward.
Software upgradeability provides for a lifetime of combat learning to be reflected in the rewriting of the software code and continually modernizing existing combat systems, while adding new capabilities over the operational life of the aircraft. Over time, fleet knowledge will allow the US Navy and its partners to understand how best to maintain and support the aircraft while operating the missions effectively in support of global operations.
Reflecting on the visit there are five key takeaways from our discussions with Navy Jax.
A key point is how the USN is approaching the P-8/Triton combat partnership, which is the integration of manned, and unmanned systems, or what are now commonly called “remotes”. The Navy looked at the USAF experience and intentionally decided to not build a the Triton “remote” operational combat team that is stovepiped away from their P-8 Squadrons.
The team at Navy Jax is building a common Maritime Domain Awareness and Maritime Combat Culture and treats the platforms as partner applications of the evolving combat theory. The partnership is both technology synergistic and also aircrew moving between the Triton and P-8
The P-8 pilot and mission crews, after deploying with the fleet globally can volunteer to do shore duty flying Tritons. The number of personnel to fly initially the Tritons is more than 500 navy personnel so this is hardly an unmanned aircraft. Hence, inside a technological family of systems there is also an interchangeable family of combat crews.
With the P-8 crews operating at different altitudes from the Triton, around 50K, and having operational experience with each platform, they will be able to gain mastery of both a wide scale ocean ISR and focused ASW in direct partnership with the surface navy from Carrier Strike Groups, ARG/MEUs to independent operations for both undersea and sea surface rather than simply mastering a single platform.
This is a visionary foundation for the evolution of the software upgradeable platforms they are flying as well as responding to technological advances to work the proper balance by manned crews and remotes.
The second key point is that the Commanders of both P-8 aviator and the soon to be operational Triton community understand that for transformation to occur the surface fleet has to understand what they can do. This dynamic “cross-deck” actually air to ship exchange can totally reshape surface fleet operations. To accelerate this process, officers from the P-8 community are right now being assigned to surface ships to rework their joint concepts of operations.
Exercises are now in demonstration and operational con-ops to explain and real world demonstrate what the capabilities this new and exciting aspect of Naval Air can bring to the fleet. One example was a recent exercise with an ARG-MEU where the P-8 recently exercised with the amphibious fleet off of the Virginia Capes.
The third key point is that the software upgradeability aspect of the airplane has driven a very strong partnership with industry to be able to have an open-ended approach to modernization. On the aircraft maintenance and supply elements of having successful mission ready aircraft it is an important and focused work in progress both inside the Navy (including Supply Corps) and continuing an important relationship with industry, especially at the Tech Rep Squadron/Wing level.
The fourth point is how important P-8 and Triton software upgradeability is, including concurrent modification to trainer/simulators and rigorous quality assurance for the fidelity of the information in shaping the future of the enterprise. The P-8s is part of a cluster of airplanes which have emerged defining the way ahead for combat airpower which are software upgradeable: the Australian Wedgetail, the global F-35, and the Advanced Hawkeye, all have the same dynamic modernization potential to which will be involved in all combat challenges of maritime operations.
It is about shaping a combat learning cycle in which software can be upgraded as the user groups shape real time what core needs they see to rapidly deal with the reactive enemy. All military technology is relative to a reactive enemy. It is about the arsenal of democracy shifting from an industrial production line to a clean room and a computer lab as key shapers of competitive advantage.
The fifth point is about weaponization and its impact. We have focused for years on the need for a weapons revolution since the U.S. forces, and as core allies are building common platforms with the growth potential to operate new weapons as they come on line. The P-8 is flying with a weapon load out from the past, but as we move forward, the ability of the P-8 to manage off board weapons or organic weapons will be enabled.
For example, there is no reason a high speed cruise or hypersonic missile on the hard points of the P-8 could not be loaded and able to strike a significant enemy combat asset at great distance and speed. We can look forward to the day when P-8s crews will receive a Navy Cross for sinking a significant enemy surface combatant.
In short, the P-8/Triton is at the cutting edge of naval air transformation within the entire maritime combat enterprise. And the US Navy is not doing this alone, as core allies are part of the transformation from the ground up.
This is the fourth piece in our series on the response to Putin’s escalatory rhetoric and force structure planning.
The featured photo shows U.S. Navy Adm. Bill Gortney providing remarks during the North American Aerospace Defense Command and U.S. Northern Command Change of Command ceremony, May 13, 2016 on Peterson Air Force Base, Colo. U.S. Air Force Gen. Lori J. Robinson was appointed by the President of the United States and the Prime Minister of Canada and confirmed by the U.S. Senate to assume command from U.S. Navy Adm. Bill Gortney. (DoD Photo by N-NC Public Affairs/Released)