By Robbin Laird
We have raised for some time the question of whether the liberal democracies can effectively crisis manage. And our colleague John Blackburn set up a new Institute in Australia a couple of years ago to focus attention on how Australia could become a more resilient society in facing significant global transitions.
With the Coronavirus pandemic we certainly are facing a global crisis. Governments are hunkering down nationally to deal with the crisis and generating their own solutions to get through the most immediate aspects of the crisis.
But which nations will rise to the task of leveraging the crisis to become more resilient in the future and to shape crisis management capabilities?
The current crisis certainly has exposed both unrealistic social expectations and political leadership shortfalls in the liberal democracies in coming to grips with crisis, as opposed to managing prosperity.
Divergent responses to the crisis across the board in the global liberal democracies will challenge the ability to shape common solutions going forward.
The underlying conflict between the 21st century authoritarian powers and the liberal democracies has been accentuated and highlighted as well. With Putin having tossed out most NGOs from Russia as part of his consolidation of power, the absence of credible information within Russia makes trust in Russia’s ability to contribute to a global management of a pandemic virtually non-existent.
The Chinese government has elevated information obfuscation an art form during the current crisis. This situation raises fundamental questions about trust with regard to China which are rooted in their domestic system going forward. And certainly, the over reliance on Chinese supply chains, a subject to which we have dedicated many articles in the past few years, is highlighted as well.
But will the liberal democracies shape lessons learned and establish more reliable supply chains?
Will the liberal democracies shape more realistic working relationships with one another to have more resilient national capabilities shared across a shared sovereign space?
During my recent visit to Australia and upon my return, I have talked at length with Blackburn and Anne Borzycki, a director of The Institute for Integrated Economic Research-Australia about shaping a way ahead.
Or put a different way, will we waste the experience of the Coronavirus crisis or can we shape lessons learned and carve a more effective way ahead to deal with future crises?
We started the conversation by noting that Australia has had a tough time of over the past few months.
Blackburn: “From an Australian perspective, we’ve been through some of the worst bushfires we’ve experienced. We’ve had floods, hailstorms, dust storms, and now a pandemic. I think that the quote I made yesterday in the post that, “Who could have ever predicted this,” as an excuse for being unprepared actually summarizes the problem we have.
“I’ve been involved myself in pandemic exercises within the military, both as a military officer and a consultant; none of this is that new. However, we didn’t take sufficient notice of a lot of that analysis, because implementing the recommendations would have been difficult politically, and we tend to defer decisions until we are in the crisis itself. We are in a situation, in my view, largely of our own creation, and our lack of preparedness and the scale of panic we see, is alarming.
Laird: The core focus is too often on the following the soccer ball rather than putting an event in context. The Coronavirus crisis is the current soccer ball, with perhaps a few soccer games, but after the season ends, the hope will be to return to the way it was.
“The challenge is whether the crisis is simply treated as a bump on the road or whether it is recognized as a turning point.
Blackburn: When you’re in the crisis it is too late to prepare for the crisis you’re in. So, how do we prepare for the next crisis? It will come for sure. How do we adapt? How do we shape a way to prevent the worst effects of a future crisis?
“The key three focus areas for moving ahead are to ‘Prepare,’ to ‘Adapt,’ and to ‘Prevent’ where possible the worst impacts of a future crisis.
“We’ve been following this free market religion that the market can actually fix everything, let’s go for the lowest cost regardless of what the end price is. Just in time supply chains result in less resilience. One of the very first things we have to do is accept that that our current model of business and global supply chains is dead. It not going to work for us, so we have to think of a new model.”
Laird: One analyst has suggested that we are going to need to shift from just in time to just in case supply chains. And as our colleague Rosemary Gibson has noted that lowest cost approach to supply can end up being the most expensive option from the standpoint of social resiliency and national security … “there is a very high price to cheap.”
Blackburn: When we redesign our supply chains, we need to pursue a “Smart Sovereignty” model. The scale or degree of sovereign capability you have in a country, will vary significantly country by country. A country the size of U.S., with its population and manufacturing capacity, will have a greater degree of sovereign capability.
“A country like Australia, with much smaller population and a different economic base will have a smaller degree of sovereignty, but we need a lot more than we have right now where we’re 90% import dependent for our fuels and we’re 90% import for our medicines.
“We also depend primarily on foreign owned shipping to move our trade; this is a major source of economic and supply chain vulnerability in times of crisis. Australia has one of the smallest nationally flagged shipping fleets in the developed world with only 14 ships of 2000 Tons or greater on the Australian register.
“What must go with Smart Sovereignty is Trusted Supply Chains. You have to have diverse supply chains, and you have to have assured yourself that you can trust them. What is evident here is the massive outsourcing and dependence upon China as the sole source of pharmaceutical ingredients and other essential supplies, cannot be ‘trusted.’ We’ve seen it fail in the current crisis.
“We need to test our supply chains. We need to verify them. Smart Sovereignty with Trusted Supply Chains is a part of addressing the problem in terms of ‘prepare, adapt and prevent.’
“We need a much more proactive approach to assuring our own sovereignty, and that’s part of the ‘prepare’ challenge. With regard to ‘adapt,’ we need to look at our supply chains and how they work. With regard to ‘prevent,’ we may need in time to exclude/replace those countries, or supply chain elements that we cannot verify and ensure they meet the required degree of trusted capability.
Laird: We are talking first of about a national strategy, but given we are all in a semi-sovereign state with regard to our economies, our security or are defense capability when considering the liberal democracies dealing with the 21stcentury authorization powers, we need to focus on how the liberal democracies can reset how they work together.
“And the question of trusted supply chains need also to be specific. Each nation needs to take a hard look at its priorities and seek out trusted partners with whom it shares common standards and can be certain that the information available is trustworthy.
“This puts an onus on the authoritarian societies which are clearly built on lack of transparency. This means that your focus requires a serious relook at how specific areas of cooperation can happen with particular countries rather than giving blank checks to the global marketplace or particular allies.
Blackburn: There has been an unwillingness at the political level in Australia to consider the risks of blind reliance on the market or how authoritarian capitalist regimes like China can impact our safety and security. We need to understand that the current crisis is yet another wakeup call and not just one to go back to sleep again after it is over.
Borzycki: In Australia, this is certainly a bipartisan problem, of being blind to the situation we have put ourselves into with regard to an inability to address our vulnerabilities as a core political task to be worked with the private sector. This crisis gives us an opportunity to rework the relationship between government and the private sector to build a resilient capability.
Laird: And this is clearly not simply a political problem; it is about unrealistic social expectations that we just get on with enjoying life and not having to face the inevitability of crises and that we are no likely to face an unchallenged road ahead with regard to international trade, commerce or military conflict.
Blackburn: We’re in the midst of a crisis that we’re trying to manage. But we also need to lay down the foundation for enhanced resilience in the future. We also need to shape more realistic expectations that crisis management is becoming a way of life and not just a “once in 50 year event.”
Borzycki: There is a unique aspect of the challenge facing Australia today. We have had basically 30 years of prosperity and economic growth. We didn’t take a hit during the GFC, so we have a generation of people, now in their forties and in leadership roles across Government and the private sector, whose entire generation’s DNA has an expectation of market growth and prosperity. The prosperity that we have experienced as a nation has become a critical cultural weakness for us as we to try survive and move forward.
Blackburn: Meeting the challenge is not simply a government responsibility. It’s a shared responsibility for governments of all levels, with industry, with the workforce, and with us as individuals.
“When I said ‘prepare, adapt, or prevent’, the ‘adapt’ is what we’re going to have a hard conversation with our whole society saying, “we’re going to have to change our expectations. This is not going to be sustainable.” We will also have to take a degree of individual responsibility for our personal and community resilience – it is not an issue that the Government can address by itself.
“We have to change our expectations, our behavior. We’re not clients of the government. We don’t have human rights for absolutely everything to be provided to us. We are citizens with a shared responsibility. We’ve got to face these facts, face reality, and change.”
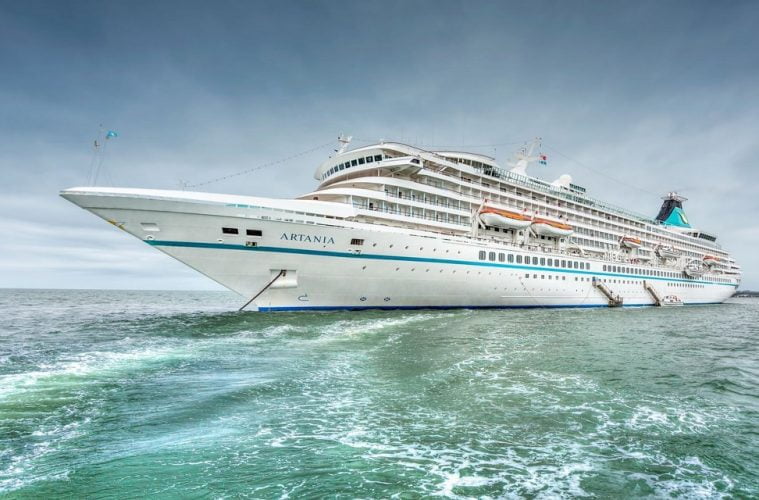
The featured photo shows the German ship, Artania.
In an article by Bernadette Chua published on March 26, 2020, the author describes how the ship has been a focus of German-Australian cooperation in the current crisis.
There are seven passengers on the German ship, Artania who have tested positive for COVID-19. While the ship has no Australians onboard, there are 800 guests and 500 crew members.
The Artania requested urgent medical assistance from West Australian authorities earlier this week and the ship’s operators have told passengers that they will be sent home on chartered flights to Frankfurt in Germany, leaving this weekend.
WA will provide hospital care for passengers with life threatening medical conditions and a man was transferred from the Artania on Thursday night with what is understood to be a heart problem.
The developments come overnight, despite Premier Mark McGowan calling on Australian Navy to get the ship out of Australian waters.
He also requested yesterday, the Commonwealth help and said if any passengers required medical attention on shore, and that they should be taken to a place away from the public.
“We’d like the Commonwealth to assist with that, we’d like those passengers…if they have to, to go into a Commonwealth facility,” Mr McGowan said.
“The Commonwealth has assets here, it has defence assets, it has the navy, we’d like their assistance to try to get the Artania to leave as soon as possible,” he said.
“There’s no Australians on board, it needs to be fuelled, but it needs to leave and go to its home port.
“Its home port is actually Germany, so what we’re saying to the ship is ‘you need to leave’, and we’re saying to the Commonwealth ‘you need to help us get that ship to leave’.
Most of the passengers on the ship are German, but Australian and Swiss passport holders will also travel to Frankfurt.
But Premier McGowan is demanding that the MSC Magnifica, which is now in limbo off the coast after being denied entry by Dubai, leave WA waters.
NSW Premier Gladys Berejiklian has also barred cruise passengers from NSW until tougher protocols are established.
Ms Berejikilian has pushed for tougher cruise ship testing after state and federal government let over 2,000 passengers off the Ruby Princess, despite a number of passengers feeling unwell.
Australian Border Force chief Michael Outram earlier this week, said the bungled decision was squarely the responsibility of NSW health and the federal agriculture department.
One passenger, a 77-year-old woman has died.
“The protocols I want far exceed what the existing protocols are and that’s what we’re negotiating with the federal government,” said Ms Berejiklian.
“I don’t want anyone coming off a ship, and I know that’s hard for some families, until the state and federal government agree on what we’re doing moving forward.”
To follow up with The Institute for Integrated Economic Research-Australia, see the following:
https://www.jbcs.co/#/iieraust/
Also, see the compilation of our recent articles on the crisis and shaping a way ahead:
The Coronavirus Crisis: Shaping a Way Ahead
03/27/2020
By Defense.Info
This report provides a compilation of our recent pieces on responses to the Coronavirus crisis, current actions, and the challenge of shaping a way ahead.